Designing optical systems with hot and cold mirrors
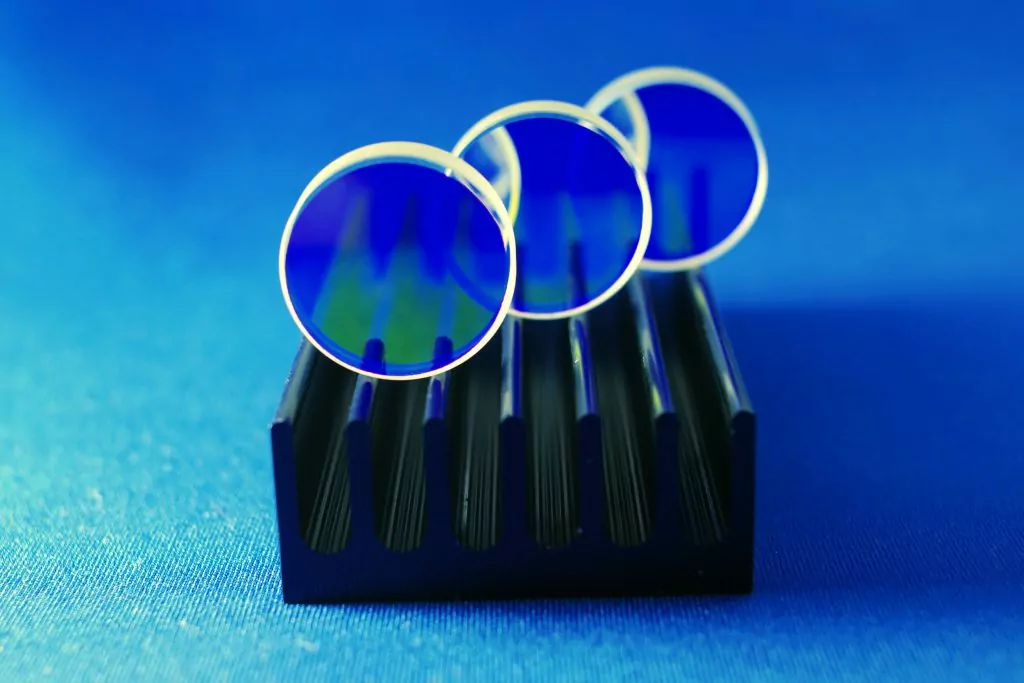

Filters for selecting specific wavelengths are common in optical systems. In our microscope design article we explained the use of dichroic mirrors to select fluorescent wavelengths. In some applications optical engineers need to filter out high (UV light) or lower frequencies (IR light). These kinds of filters are called “Hot and Cold mirrors” . For […]
Master Lighting Design: Understand Radiometric vs. Photometric Data for Perfect Illumination
In the world of lighting design, we encounter a variety of metrics that describe the performance and effectiveness of a light source. Recently, we had a customer provide an illumination specification in watts, which is a radiometric unit, but for applications involving human vision, such as architectural lighting or display technologies, optical engineers typically work […]
Understanding Free Space Optical Communication Design
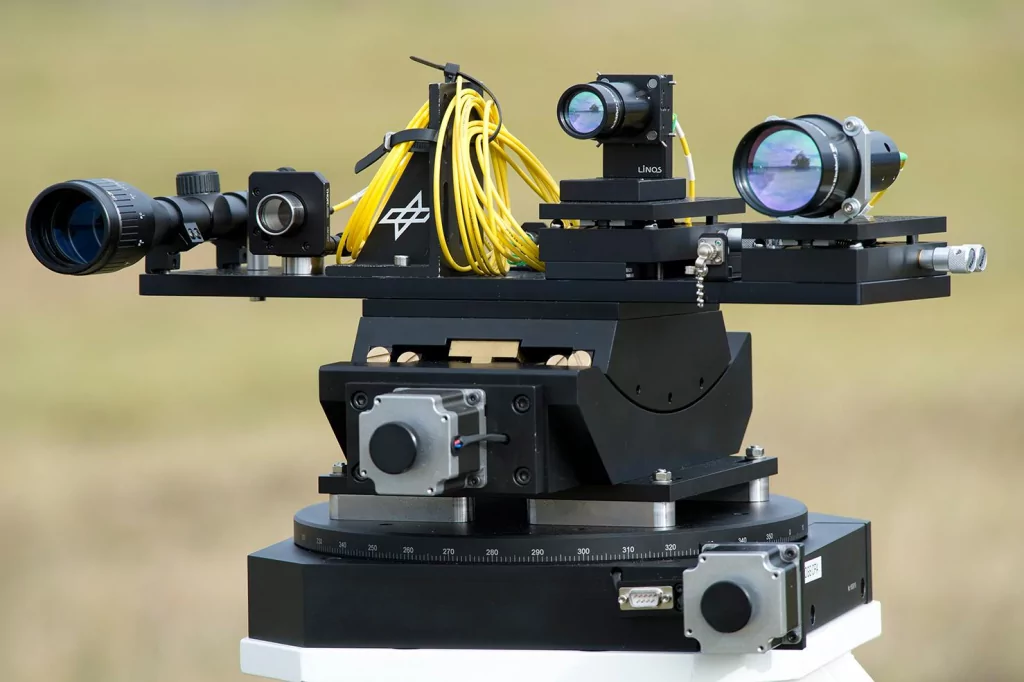

A previous post discussed underwater optical design. This week, we will review the diametrical opposite application – free-space optical communication (FSO). As with underwater optical design, one of the challenges facing FSO is the optical signal propagation through a highly variable medium. For example, atmospheric turbulence produces temporary pockets of air with slightly different indices […]
Parabolic Mirror Design
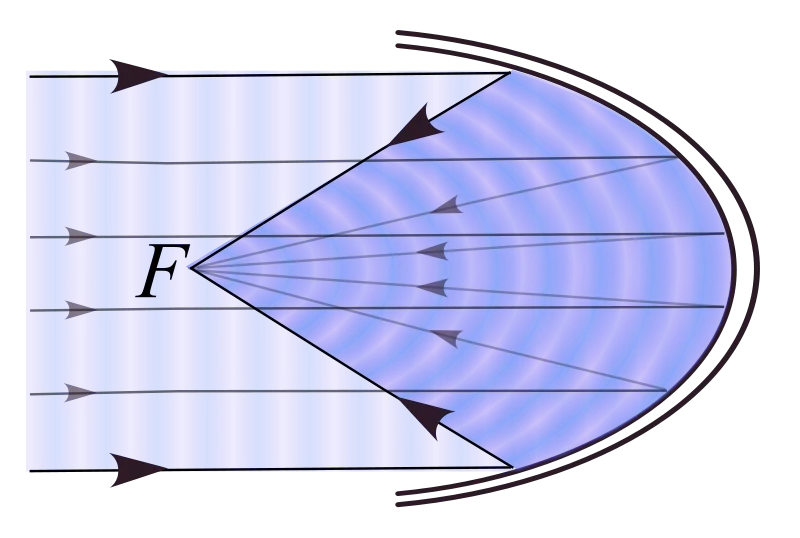
Parabolic mirrors are optical systems that are used to collect or distribute energy. They have a wide range of applications from solar collectors for water heating systems to microscopes and telescopes, and everyday flashlights. The most common way to understand parabolic mirrors is that a bundle of light beams parallel to the optical axis will […]
5 things to know about refractive index
Introduction The refractive index is one of the basic concepts in optical sciences. Same as volume, and density, the refractive index is a fundamental property of all materials. However, not only materials that are used in optics have a refractive index. For example, the refractive index of water is 1.33, and the refractive index of […]
What is Birefringence?
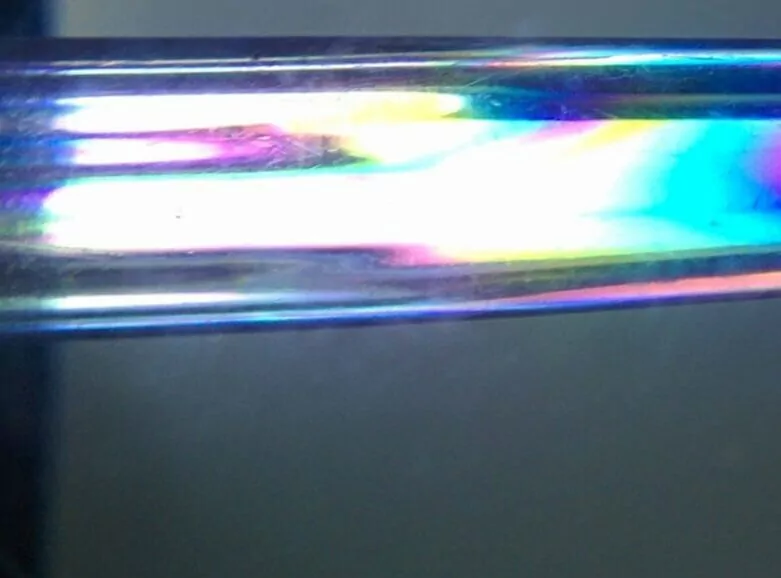

In a previous post, we explained the concept of a material refractive index in optics in the context of optical design. Something that we didn’t review however is that many materials have two, three (and even more) different refractive indices depending on the direction and polarization of light. This is a very interesting (and often […]