Working principle of TIR lenses
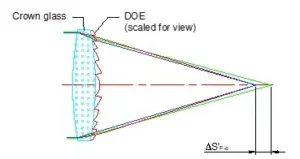
A TIR lens works on the principle of total internal reflection. When light reaches an interface between two materials with different refractive indices and the correct angle of incidence, there is refraction (bending of a light ray from its original path).
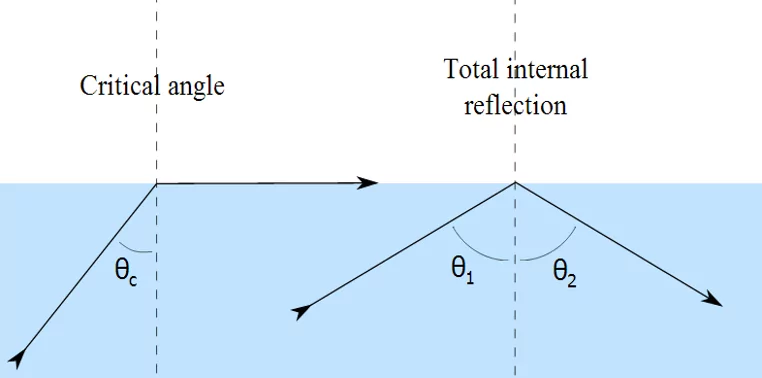
As light travels from a medium with a higher refractive index to that with a lower one, Snell’s law requires the angle at which the light ray gets refracted to be greater than 90 degrees.
For angles of incidence exceeding a particular value, the light is reflected into the material.
The angle for which this occurs is called the critical angle and the phenomenon is called total internal reflection
Total internal reflection (TIR) ensures no associated loss of power, making it the most efficient method for reflecting light. Therefore, the design of lenses utilizing TIR principles takes full advantage of this physical property.
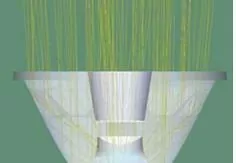
When placed on top of an LED chip, the optical component is able to capture and direct the photons to the desired location.
Compared with other methods of controlling LED light, such as a reflector, this optical component provides better light control since it captures all of the photons leaving the source.
If you need a custom lens design or advice from an experienced optical engineer, click here to learn more about our work in LED and illumination optics.

Different TIR lenses are used for different purposes. Depending on the design requirements, you might use a TIR lens for a narrow spot, wide spot, elliptical, or a medium spot for a specific USDOT streetlight.
As a general rule, the smaller the desired beam angle, the larger the size of a TIR lens or reflector needs to be. This is because of etendue.
TIR lenses can be machined out of acrylic for prototyping purposes but generally are injection molded in volume. A custom TIR lens design could cost between $4,000- $15,000 depending on the design complexity, with asymmetrical light patterns requiring more design time than symmetrical ones.
The cost of a mold for production can be $3,000- $30,000 depending on the type ( aluminum or steel), number of cavities in the mold, and the size of the required optic. When produced in volume, a custom TIR lens could cost $0.50- $3.00 per item.
Want to learn more about LED optics? This post on the 5 best materials for LED optics might be of interest.
FAQs: TIR Lens Design
What is a TIR lens?
A TIR (Total Internal Reflection) lens is an optical component that uses total internal reflection to collect and redirect light, most commonly from an LED source. It combines refraction and internal reflection to efficiently shape and control the output beam.
How does total internal reflection work in a TIR lens?
Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a higher refractive index material to a lower one at an angle greater than the critical angle. Instead of refracting, the light is fully reflected inside the material, allowing efficient beam shaping without reflective coatings.
Why are TIR lenses efficient for LED illumination?
TIR lenses can capture nearly all photons emitted by an LED and redirect them toward the target area. Unlike traditional reflectors, TIR optics minimize light loss and provide precise control over beam shape and angular distribution.
How do TIR lenses compare to reflectors?
Compared to reflectors, TIR lenses offer better optical efficiency, improved beam control, and more compact designs. Reflectors can suffer from scattering and coating losses, while TIR lenses rely on internal reflection with minimal power loss.
What beam patterns can be achieved with TIR lenses?
TIR lenses can be designed to produce narrow spot, wide spot, medium spot, elliptical, or highly asymmetric beam patterns. The final beam shape depends on the lens geometry and the optical requirements of the application.
Why do narrow beams require larger TIR lenses?
Narrow beam angles require larger optics due to etendue conservation. To collimate light more tightly, the lens must have sufficient aperture size to collect and redirect the emitted light without excessive losses.
What materials are commonly used for TIR lenses?
TIR lenses are commonly made from optical-grade plastics such as acrylic or polycarbonate. Acrylic is often used for prototyping and high-optical-quality applications, while injection-molded plastics are preferred for high-volume production.
How are TIR lenses manufactured?
Prototypes are typically CNC-machined from plastic, while production lenses are injection molded. Injection molding enables consistent optical quality and low per-unit cost when produced at sufficient volume.
When is a custom TIR lens design required?
Custom TIR lenses are needed when standard optics cannot meet beam shape, efficiency, regulatory, or mechanical constraints. Asymmetric illumination patterns and application-specific beam control often require fully custom optical design.
What factors influence the cost of a custom TIR lens?
Cost depends on optical complexity, symmetry of the beam pattern, tolerance requirements, material choice, and production volume. Asymmetric designs and tight angular control typically increase both design and tooling costs.